From Shores & Households to Markets: Dynamics of Seaweed Farming in Tanzania

This Policy Brief identifies opportunities and challenges for expanding seaweed farming in Mainland Tanzania and Zanzibar, while strengthening sector resilience. READ ON…!
Learning from the Experience of the Namibian Blue Economy 2

This Policy Brief outlines some lessons from the experiences of Namibian blue economy following the mission of REPOA and the Bank of Namibia teams, which met the relevant Government authorities and the private sector agencies there. READ ON…!
Gender equality and women’s empowerment: The unintended consequence of women’s access to the labour market
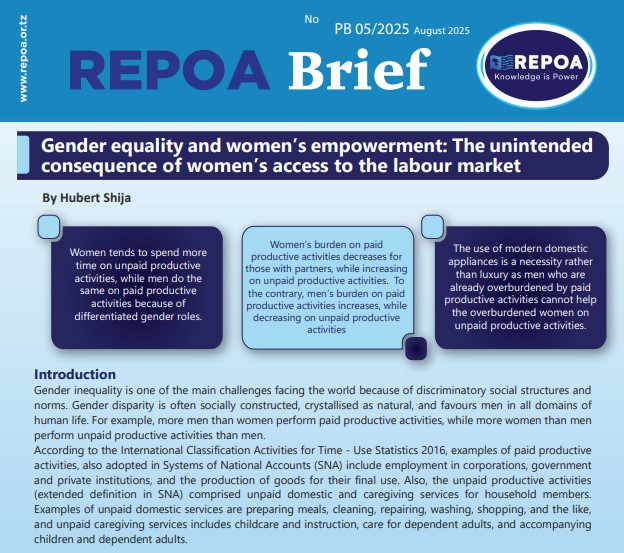
This Policy Brief compares the relative workloads of women and men based on a workload limit of 10:30 hours a day according to the Women’s Empowerment in Agriculture Index (WEAI) to inform the gender related policies. Read ON…!
The role of the services economy and trade in economic structural transformation and development trajectory in Tanzania

This Research Report provides a comprehensive overview of Tanzania’s position in the global economy, including its level and changes, through the lens of Gross Value Chains (GVCs), with a focus on the service sector. Studying the Tanzanian experience is not only interesting for its policy implications, but also because Tanzania is representative of small, open […]
Intrahousehold bargaining and Climate-Smart Agriculture: Productivity outcomes among female paddy farmers in Morogoro, Tanzania
This study explores the drivers of women’s bargaining power in households, and their impact on Climate-Smart Agriculture (CSA) practices adoption in Tanzania, focusing on paddy production. The study uses data from 317 women farmers. Results reveal that, the adoption of CSA practices is influenced by factors such as women’s bargaining power, age, non-farm income, area […]
Unlocking the Blue Economy: Insights from the Fisheries Sector in Coastal Mainland Tanzania and Zanzibar
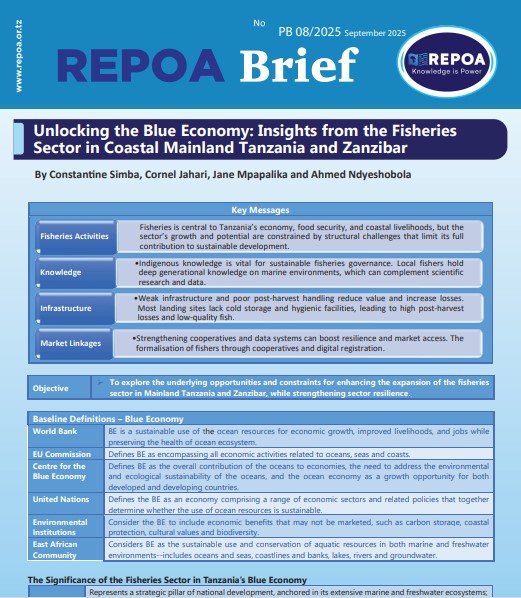
This Policy Brief explores the underlying opportunities and constraints for enhancing the expansion of the fisheries sector in Mainland Tanzania and Zanzibar, while strengthening sector resilience. READ ON…!
Learning from the Experience of the Namibian Blue Economy 1

This Policy Brief outlines some lessons from the experiences of Namibian blue economy following the mission of REPOA and Bank of Namibia teams, which met with the relevant Government authorities and the private sector agencies there. READ ON…!
Building on Productive Capacities in Tanzania-Opportunities and Constraints in the Horticulture Sub-Sector

This Policy Briefs explores the underlying opportunities and constraints for enhancing the expansion of productive capacities in the horticulture sub-sector for industrial and trade expansion in Tanzania. For details please, READ ON…!
Harnessing Tanzania’s Services Trade for Structural Transformation

This Policy Brief presents key findings from a study that investigated the impact of changes in the composition of services and trade sub-sectors on economic growth and transformation in Tanzania. Specifically, it offers a picture of Tanzania’s services trade profile and analyse the contribution of services trade to GVCs through decomposition of value added in […]
Dynamics of Service Sector in Tanzania and its role in structural transformation

The service sector in Tanzania has become increasingly dominant in the country’s economic landscape, significantly contributing to GDP and offering potential avenues for inclusive and sustainable economic growth. This policy brief examines the evolution of the service sector, identifies key opportunities, and present econometric results on the drivers of the service sector expansion for the […]
Building productive capacities in Tanzania—opportunities and constraints in the coffee sub-sector

It is recommended that this framework of analysis is adapted to inform policy analysts, private sector practitioners, and decision makers in public institutions responsible for promoting economic growth; agriculture and cooperative development; investments, trade, and industrial development; private sector development, and providing the requisite political champion for the coffee sub-sector. It is the ability these […]
Trust in tax administration: Why it matters for tax compliance
Trust is a foundational component of any tax system, particularly in environments where enforcement capacity is weak. In Tanzania, businesspeople exhibit low levels of trust in tax authorities, undermining voluntary compliance and weakening the legitimacy of the tax system. However, trust is not static; it can be built – and rebuilt – through better services, […]
To trust or not to trust? Taxation from the perspective of businesspeople in Tanzania

Given the limited capacity for effective tax enforcement and monitoring in developing countries, taxpayers’ trust in the tax system is essential for fostering voluntary tax compliance. Since businesses account for a substantial portion of tax revenues, this paper examines the factors that predict trust in the tax authority, drawing on a large-scale survey of businesspeople’s […]
REPOA’s Annual Report 2024

Dear Esteemed Stakeholders, we are pleased to present to you our Annual Report for 2024, which offers a comprehensive account of the performance and results achieved during the final year of implementation of REPOA’s Strategic Plan 2020-2024. This report reflects our continued commitment to undertaking impactful research, strengthening capacity for research and evidence use, and […]
Urban Motorcycle Taxi -related crimes in Dar es Salaam and Pwani Regions, Tanzania

The overall aim of this policy brief is to offer a better understanding of the crime situation within the context of motorcycle taxi riding, assess the coping capacities of stakeholders, and suggest strategies to alleviate the associated crimes. The study was conducted in Dar es Salaam city and three urban centres in Pwani region: Kibaha, […]
Addressing Disparities in Local Economic Development Implementation across Councils in Tanzania

This policy brief explores these disparities and provides actionable recommendations to harmonize Local Economic Development (LED) implementation across councils. This policy brief aims to shed light on the underlying factors contributing to the disparities in LED implementation between urban and rural councils in Tanzania. By examining the specific challenges faced by rural councils, such as […]